Pep Guardiola is considered one of the most influential managers in football history. He brought about revolutionary changes in tactics and philosophy, redefining the modern game. His football ideology and style can be summarized as follows:

1. Pep Guardiola’s Football Philosophy
Pep’s philosophy is deeply rooted in “Positional Play.” It emphasizes not just technical skill but also maximizing space, positioning, and team harmony.
- Spatial Awareness: Players occupy optimal spaces on the field to break down opposition pressure and enhance attacking efficiency.
- Possession-Based Football: High ball possession dominates the game, minimizing the opponent’s opportunities.
- Decision-Making and Patterns: Quick decision-making and diverse play patterns keep the opponent guessing and disorganized.
2. Key Tactical Features of Pep Guardiola’s Style
While Guardiola’s tactical style varies slightly depending on the team and era, it has always been innovative and progressive.
(1) Refinement of Tiki-Taka
- At Barcelona, Pep perfected Tiki-Taka, focusing on short, quick passes and movement to dismantle defensive structures.
- Key Players: Xavi Hernandez, Andres Iniesta, and Lionel Messi formed the core of this system with their exceptional technical ability and understanding.
(2) Inverted Fullbacks
- At Manchester City, Guardiola introduced the concept of inverted fullbacks, where fullbacks move into central midfield roles rather than overlapping on the flanks.
- This creates numerical superiority in midfield, neutralizing opposition pressing.
(3) False Nine
- During his Barcelona tenure, Pep used Lionel Messi as a “False Nine,” confusing opposition defenders and allowing Messi to roam freely, creating space and chances.
- This tactical innovation has since influenced many teams and managers.
(4) Exploitation of Half-Spaces
- Guardiola emphasized the use of half-spaces (the areas between the flanks and central zones) to bypass defensive lines and execute creative attacks.
(5) Pressing and Counter-Pressing
- His teams excel in immediate, aggressive pressing after losing possession, known as counter-pressing, to regain the ball quickly and nullify counterattacks.
3. Impact of Pep’s Innovations on Football
(1) Focus on Spatial Thinking
- Pep’s tactics shifted football’s focus from individual brilliance to the collective use of space, which has become a staple of modern football.
(2) Tactical Flexibility
- Guardiola demonstrated the ability to adapt and evolve his tactics depending on opponents and circumstances, inspiring other managers to embrace flexibility.
(3) Player Development
- Pep emphasizes not only winning but also improving individual players’ technical skills and tactical understanding. He has transformed many players into new roles with great success.
4. Key Achievements by Club
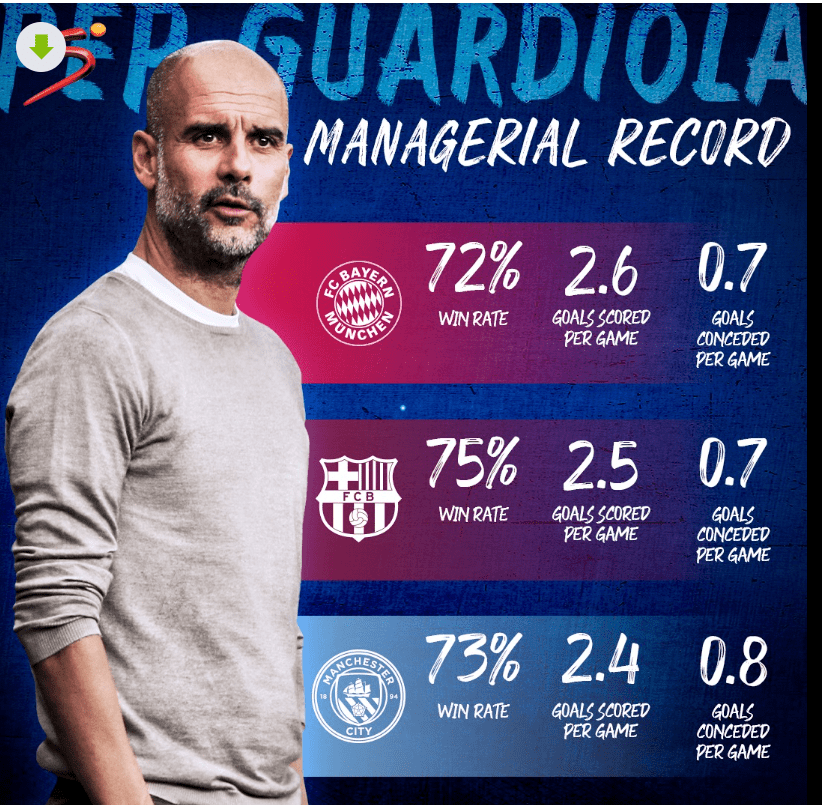
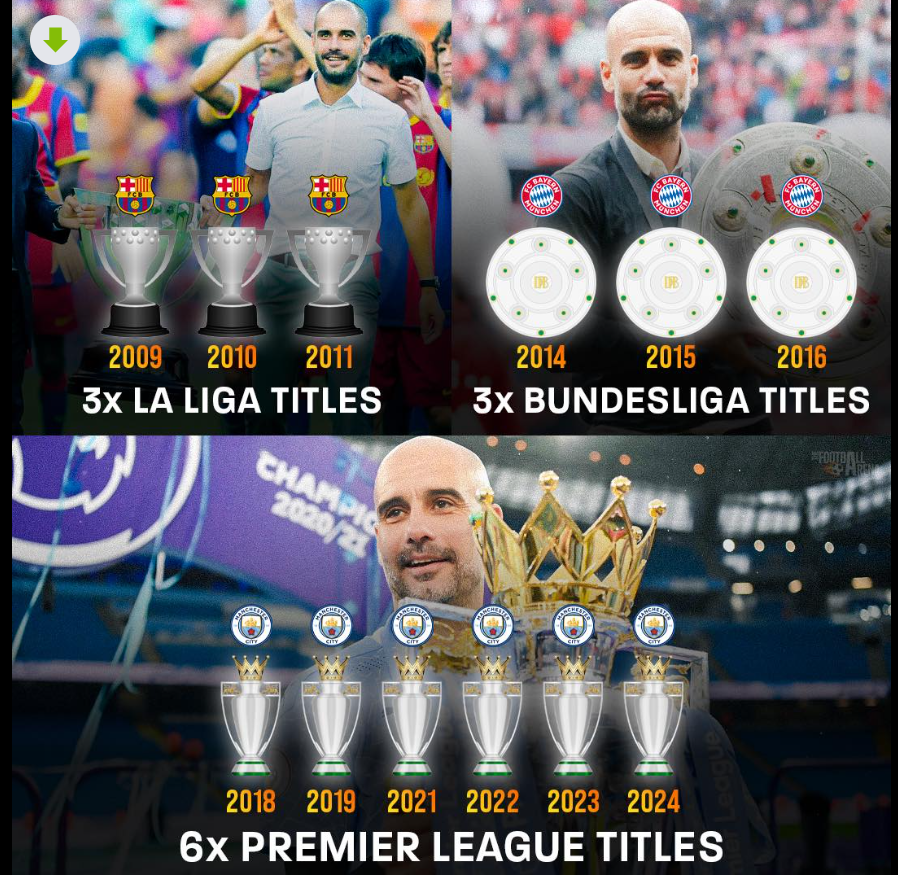
(1) FC Barcelona (2008–2012):
- 3 La Liga titles and 2 UEFA Champions League titles.
- Established Tiki-Taka as a global phenomenon and set a new benchmark for football.
(2) Bayern Munich (2013–2016):
- 3 Bundesliga titles.
- Introduced positional play and possession-based football to German football.
(3) Manchester City (2016–Present):
- 5 Premier League titles (as of 2023).
- Elevated tactical standards in English football while dominating the league.
5. Conclusion
Pep Guardiola is not just a football manager; he is a revolutionary who redefined the game itself. His philosophy and tactics have shaped the course of modern football and will continue to inspire managers and players for years to come.
Key Tactics and Plays of Pep Guardiola’s Evolution of Total Football
Pep Guardiola has taken the foundations of Total Football, a philosophy introduced by Rinus Michels and Johan Cruyff, and elevated it to new levels of tactical sophistication. Below are the key tactics and plays that define Guardiola’s version of Total Football:
1. Positional Play (Juego de Posición)
- Concept: Positional Play is at the core of Guardiola’s philosophy. Players are required to occupy specific zones on the pitch to create numerical and spatial advantages.
- Key Elements:
- Triangles and Passing Lanes: Players form constant triangles to provide multiple passing options.
- Zone Occupation: No two players should occupy the same zone, ensuring proper spacing and balance across the pitch.
- Progression Through the Thirds: The team builds from the back, advancing the ball through midfield with patience and precision.
2. High Pressing and Counter-Pressing
- High Pressing: Guardiola’s teams press intensely in the opponent’s half to regain possession as quickly as possible. This prevents the opposition from organizing counterattacks.
- Counter-Pressing (Gegenpressing): When possession is lost, the team immediately pressures the ball carrier to win it back, often within seconds.
- Objective: Disrupt the opposition’s rhythm and regain control high up the pitch.
3. Inverted Fullbacks
- Guardiola revolutionized the use of fullbacks by having them drift into central midfield positions rather than hugging the touchline.
- Benefits:
- Provides numerical superiority in midfield.
- Helps in ball circulation and controlling the tempo.
- Creates defensive stability by narrowing gaps during transitions.
4. False Nine and Fluid Attack
- Guardiola popularized the false nine role, particularly through Lionel Messi at Barcelona.
- Concept: The striker drops deep into midfield, pulling defenders out of position and creating space for wingers or midfield runners to exploit.
- Result: Opposition defenses are destabilized, leading to more attacking opportunities.
5. Utilization of Half-Spaces
- Guardiola emphasizes exploiting half-spaces—the areas between the central and wide zones.
- Why It Works:
- Half-spaces are difficult for defenders to cover.
- These areas allow for dangerous crosses, through balls, and link-up play.
- Players like Kevin De Bruyne and Ilkay Gündogan thrive in these zones, creating numerous chances.
6. Building from the Back
- Guardiola’s teams prioritize playing out from the back, using short, precise passes to evade the opponent’s press.
- Role of the Goalkeeper: The goalkeeper often acts as an additional outfield player, offering a passing option and initiating attacks.
- Defenders’ Role: Center-backs are highly technical and capable of carrying the ball forward or delivering accurate long passes.
7. Dynamic Midfield Roles
- The midfield is the engine of Guardiola’s system, with players tasked to control tempo, retain possession, and create opportunities.
- Key Features:
- Deep-lying playmakers (e.g., Sergio Busquets, Rodri) dictate play from deep positions.
- Advanced midfielders exploit gaps between the lines and link up with forwards.
8. Rotational Movement
- Players frequently rotate positions to confuse the opposition and create space.
- Example: A winger moves centrally, allowing a fullback or midfielder to overlap into wide areas.
9. Control and Patience
- Guardiola’s Total Football emphasizes controlling the tempo of the game and being patient in attack.
- The focus is on high-quality chances rather than rushing forward recklessly.
10. Adaptability
- Guardiola has adapted his Total Football principles to suit different leagues, teams, and players.
- At Barcelona: Focused on Tiki-Taka and the False Nine.
- At Bayern Munich: Integrated width and directness into the system.
- At Manchester City: Perfected positional play with tactical innovations like inverted fullbacks and dynamic attacking patterns.
Conclusion
Pep Guardiola’s evolution of Total Football combines positional discipline, intense pressing, and fluid attacking movements. By blending technical mastery, tactical intelligence, and innovation, Guardiola has redefined modern football and solidified his legacy as a true visionary of the sport.